Oral health is a vital part of overall well-being, yet many people overlook early symptoms until they become serious. In the United States, millions of adults struggle with tooth decay, cavities, gum disease, and tooth sensitivity, making them some of the most widespread health concerns. Nearly 90% of U.S. adults have cavities. In my opinion, this shows how oral health often gets ignored until it’s too late.
These conditions not only affect your smile but can also lead to infections, pain, and long-term complications if ignored. From bad breath (halitosis) to oral cancer, dental problems progress silently and often go untreated. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and prevention strategies for the 9 common dental diseases can help you protect your teeth and gums for life.
What Causes Common Dental Diseases?
Dental diseases often begin quietly. Poor oral hygiene is a major factor, as skipping brushing or flossing allows dental plaque to build up, which leads to cavities and gum disease. However, lifestyle choices such as smoking, drinking sugary drinks, and eating highly processed foods make matters worse.
Some medical conditions, like diabetes, weaken the body’s ability to fight oral infection, leaving teeth and gums more vulnerable. Genetics, age, and even medication side effects, such as those that cause dry mouth (Xerostomia) can increase risk.
Dentists frequently stress that prevention is easier than treatment. For example, plaque begins forming within hours of a meal, but it can take months for signs of cavity formation to appear. This means regular brushing, flossing, and professional cleaning remain the strongest defenses against the development of 9 common dental diseases.
Warning Signs and Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore
Many people underestimate early oral health issues because the discomfort often feels minor at first. However, even small warning signs should never be ignored. Your mouth provides early clues about conditions like gum disease, tooth decay, or even systemic problems affecting the whole body. Recognizing symptoms early can save not only your smile but also your long-term health.
- Subtle dental problems often progress silently until they become severe and harder to treat.
- Early warning signs include toothache, bleeding gums, and pain from sensitive teeth.
- Additional symptoms may involve persistent bad breath (halitosis), swollen gums, mouth ulcers, or loose teeth.
- The American Dental Association reports that nearly 50% of U.S. adults show symptoms of gum inflammation, yet many postpone care.
- Untreated issues can lead to periodontitis, dental abscess, tooth loss, or even systemic infections spreading beyond the oral cavity.
- Oral health often mirrors overall body health, making dental symptoms important indicators of broader medical concerns.
- Dentists recommend regular checkups for early diagnosing oral diseases before they become complex and expensive to manage.
- Acting early makes treatment more effective, affordable, and less painful.
Tooth Decay (Cavities)
Tooth decay is the most widespread dental issue in the United States, affecting people of every age group. According to the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR), nearly 90% of adults aged 20–64 have experienced cavities, and about 1 in 4 adults currently has untreated decay. Children are not spared either over 50% of children aged 6–11 show signs of cavity formation, making this a nationwide concern.
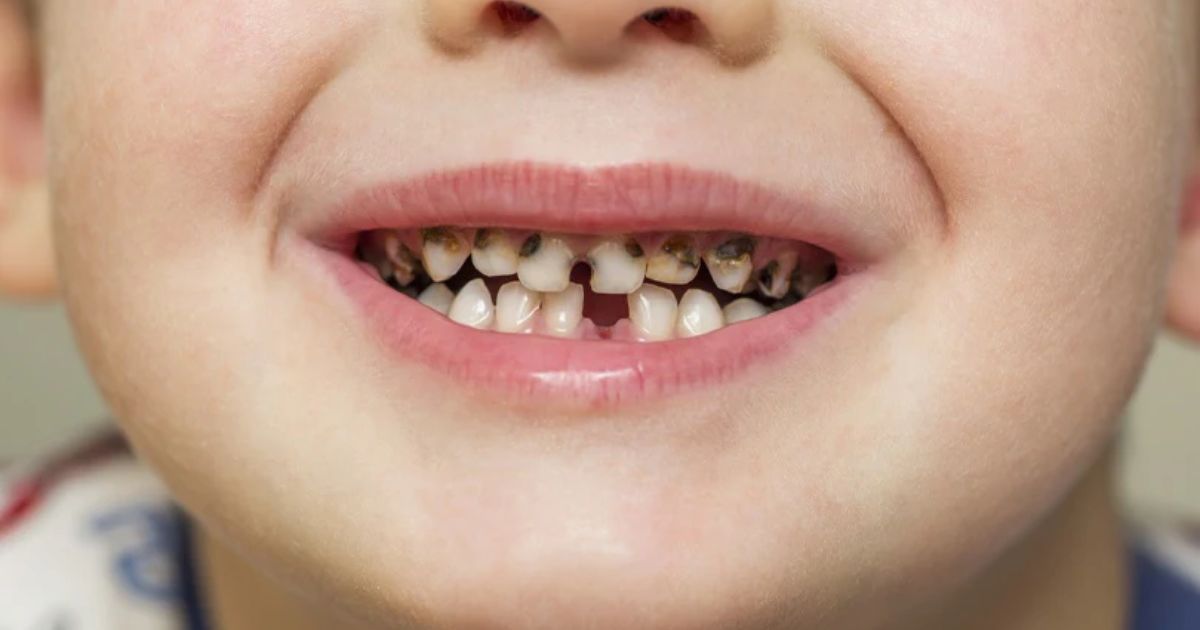
How Tooth Decay Develops in the Mouth?
This condition develops when harmful bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars and starches left behind from food. The bacteria produce acids that attack the tooth enamel, leading to enamel erosion, weak spots, and eventually holes in the teeth. If untreated, decay progresses to deeper layers, causing oral infection, severe toothache, and sometimes a painful dental abscess.
Misconceptions About Who Gets Cavities
A widespread misconception is that only children are vulnerable to cavities. In reality, adults also face high risks due to gum recession, dry mouth caused by medications, and lifestyle habits like frequent snacking on sugary foods. Untreated decay remains one of the most dangerous dental disease risk factors, often leading to tooth loss in middle-aged and older adults.
Treatments for Different Stages of Tooth Decay
Treatment depends on the severity of the decay. Early-stage cavities can be treated with fluoride varnish or small fillings, while moderate decay requires larger fillings or crowns. Advanced cases often need root canal therapy or even tooth extraction if the damage is extensive.
Prevention Strategies Against Tooth Decay
Dentists strongly emphasize tooth decay prevention strategies because prevention is always better than invasive treatments. The most effective habits include brushing twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, reducing sugar intake, and limiting acidic beverages like soda and citrus juices. Regular dental visits allow for early detection of decay before it causes major damage, saving both money and pain in the long run.
Gum Disease (Gingivitis and Periodontitis)
Gingivitis starts as mild swelling and bleeding during brushing. If untreated, it may progress to periodontitis, which causes gum recession, bone loss, and eventually missing teeth. CDC data shows 47% of adults over 30 in the U.S. suffer from some form of gum disease, making it one of the most serious among the 9 common dental diseases.
Treatment ranges from professional cleanings to scaling and root planing, and in severe cases, surgical interventions. Preventing gum problems involves controlling dental plaque, improving diet, and seeking early treatment to avoid preventing gum recession from worsening. As dentists say, “Healthy gums are the foundation of a healthy smile.”
Tooth Sensitivity
If sipping iced water or hot coffee makes you wince, you may have tooth sensitivity. This happens when enamel thins out or gums recede, exposing dentin. The exposed nerves trigger pain from sensitive teeth whenever you eat hot, cold, or sweet foods. Causes include overbrushing, enamel erosion, and untreated cavities.
Dentists recommend desensitizing toothpaste, fluoride treatments, and avoiding highly acidic foods to ease sensitivity. In advanced cases, bonding or gum grafts may help. Since tooth sensitivity is often a symptom of other conditions, addressing it early prevents further dental complications.
Cracked, Chipped, or Broken Teeth
A cracked or chipped tooth is not only a cosmetic issue; it can lead to oral infection if bacteria enter through fractures. Causes include trauma, biting hard objects, and long-term teeth grinding. Athletes, for instance, often experience cracked teeth after impact injuries.
Treatment depends on severity, minor chips may be repaired with bonding, while larger cracks require crowns or implants. If neglected, fractures can result in treatment for tooth abscess, which is painful and costly. Protecting teeth with mouthguards and avoiding habits like chewing ice are practical steps to prevent such injuries.
Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Persistent bad breath (halitosis) affects both confidence and relationships. While poor oral hygiene is the main culprit, dry mouth (Xerostomia), gum disease, and undiagnosed oral infection can all cause it. Studies show over 65% of Americans experience halitosis at least occasionally, highlighting its prevalence.
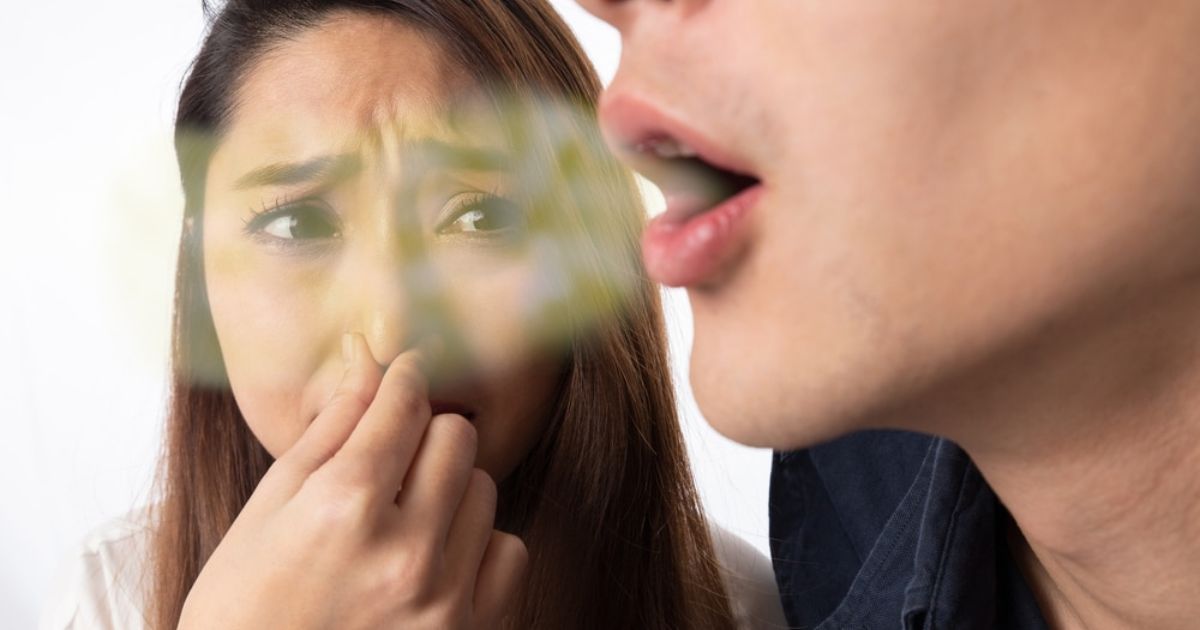

Dentists recommend improving brushing and flossing, cleaning the tongue, and staying hydrated. When halitosis doesn’t improve with hygiene changes, it often points to deeper dental disease risk factors, which require professional diagnosis and care.
Tooth Erosion and Enamel Loss
Enamel erosion occurs when acids wear away the tooth’s protective layer, leading to tooth enamel loss. Common causes include acidic foods, frequent soda consumption, and even medical issues like GERD. Once enamel is lost, it doesn’t grow back, leaving teeth vulnerable to cavities and sensitivity.
The causes of enamel erosion often relate to diet and lifestyle, meaning prevention is possible. Dentists recommend rinsing with water after acidic meals, avoiding aggressive brushing, and using fluoride to strengthen enamel. By adopting these habits, patients can significantly reduce their risk of erosion-related dental problems.
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
Dry mouth (Xerostomia) feels like sticky saliva, difficulty swallowing, or constant thirst. This condition is common in older adults and those taking medications for blood pressure or depression. Without adequate saliva, teeth lack protection, raising the risk of cavities and oral infection.
Effective management of dry mouth includes drinking water frequently, chewing sugar-free gum, or using artificial saliva products. Dentists may also adjust treatment plans for patients with chronic dry mouth to reduce complications.
Oral Cancer: The Most Serious of the 9 Common Dental Diseases
Among the 9 common dental diseases, oral cancer is by far the most life-threatening. According to the American Cancer Society, about 54,000 Americans are diagnosed with oral or oropharyngeal cancers each year, and nearly 11,000 die from the disease annually. Unlike cavities or gum disease, oral cancer can spread quickly and affect essential functions like breathing, chewing, and speaking.
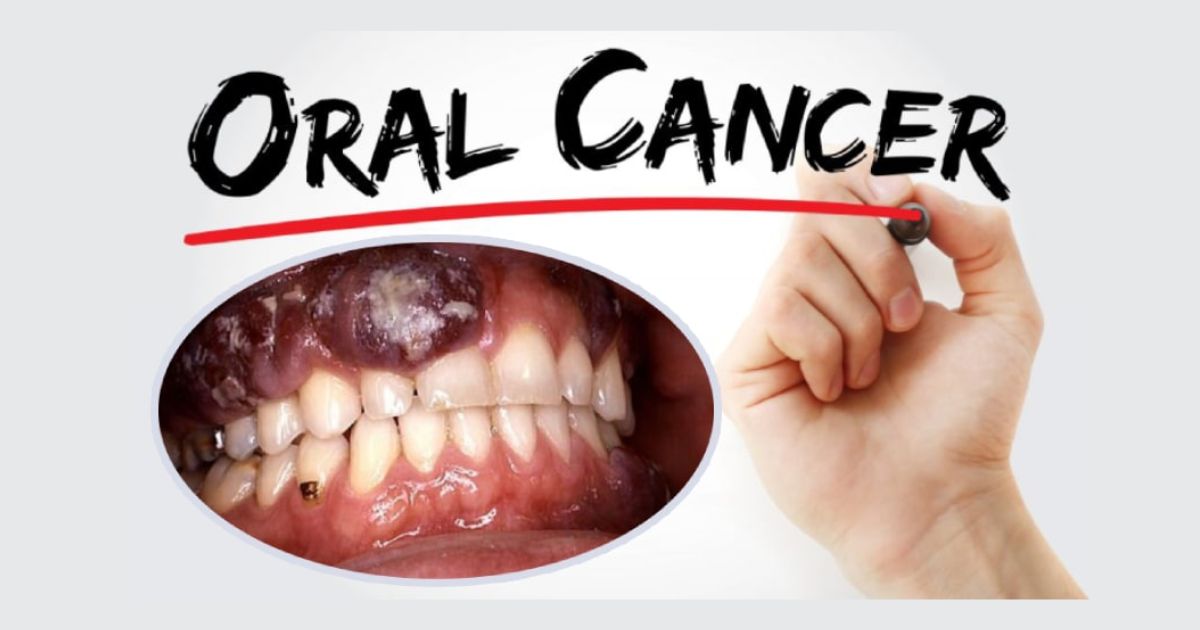
High-risk factors include smoking, heavy alcohol use, HPV infection, poor oral hygiene, and even prolonged sun exposure (linked to lip cancer). Men are twice as likely as women to be diagnosed, and the risk increases significantly after the age of 40.
Early Warning Signs for Oral Cancer
Dentists emphasize the importance of awareness, as early treatment dramatically improves survival. Watch for symptoms such as:
- Non-healing mouth sores lasting more than two weeks
- Red or white patches inside the mouth
- Difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Persistent sore throat or hoarseness
- Lumps, swelling, or numbness in the mouth or neck
Oral Cancer Risk and Survival Rates (U.S. Data)
| Risk Factor | Increased Risk Level | Notes |
| Smoking / Tobacco Use | 6x higher | Strongest known risk factor |
| Heavy Alcohol Use | 2–3x higher | Combined with smoking, risk multiplies |
| HPV Infection | Rising cases in younger adults | Often linked to throat cancers |
| Poor Diet / Oral Hygiene | Moderate | Can weaken immune defenses |
| Prolonged Sun Exposure | High for lip cancer | Common in outdoor workers |
Why Early Screening Matters
The 5-year survival rate for oral cancer is nearly 85% when detected early, but it drops to about 40% in advanced stages. This is why regular dental checkups are crucial. Dentists often remind patients: “Your dentist may save your life, not just your smile.”
Impacted or Misaligned Teeth
Impacted teeth, especially wisdom teeth issues, occur when teeth don’t emerge properly. This can cause pain, swelling, or crowding. Similarly, misaligned teeth may lead to bite problems, difficulty cleaning, and long-term toothache. Both conditions increase the risk of gum disease and decay due to cleaning challenges.
Treatment options include orthodontic braces, clear aligners, or surgical removal in the case of impacted teeth. Addressing these problems not only improves aesthetics but also reduces the likelihood of future oral infection and jaw strain.
Prevention Tips to Protect Your Oral Health
Maintaining oral health is a lifelong commitment, not just a short-term effort. Simple daily practices such as brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing, and scheduling routine dental checkups form the foundation of a healthy mouth. Also, dentists recommend flossing daily, but in my experience, even flossing three times a week makes a noticeable difference in gum health. A balanced diet with fewer sugary snacks, along with quitting smoking or chewing tobacco, helps reduce the risk of dental abscess, tooth decay, and even oral cancer.
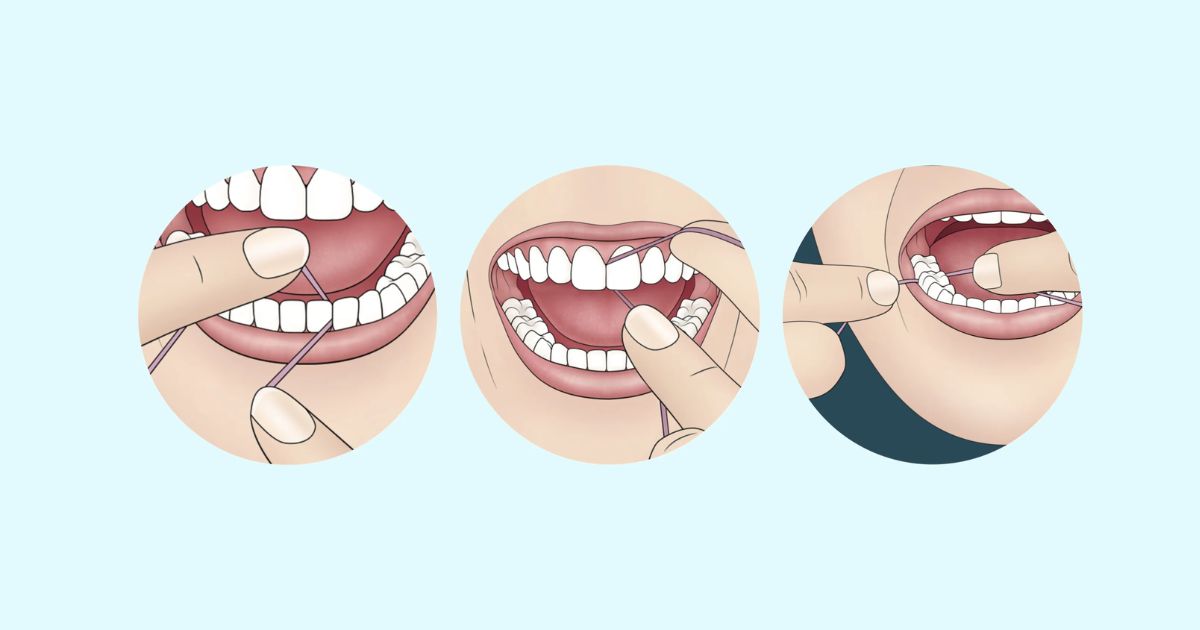
Daily Oral Care Habits
Dentists recommend brushing for two minutes twice daily and flossing at least once a day to remove dental plaque and prevent gingivitis. Using a fluoride mouthwash can provide additional protection against tooth enamel loss and cavities.
Nutrition and Diet Choices
What you eat directly affects your oral health. Diets high in sugar and acidic foods contribute to enamel erosion and cavities, while a diet rich in calcium, vitamin D, and fiber supports stronger teeth and gums. Drinking plenty of water also helps wash away bacteria and maintain saliva production.
Avoiding Tobacco and Alcohol
Tobacco products increase the risk of gum disease, bad breath (halitosis), and oral infections, while heavy alcohol use is linked to early warning signs for oral cancer. Quitting or reducing these habits improves oral and overall health significantly.
The Role of Preventive Dentistry
Dentists stress that tooth decay prevention strategies and gum care should begin early, ideally in childhood. Preventive dentistry not only reduces discomfort but also lowers long-term treatment costs. Studies show that every dollar spent on preventive care can save up to $50 in future restorative dental treatments.
When to See a Dentist for Dental Problems
Don’t wait until pain becomes unbearable. Visit a dentist if you notice swelling, bleeding, severe toothache, or sudden trauma such as a cracked or chipped tooth. Regular visits help catch issues before they escalate into more serious conditions.
Even without symptoms, twice-yearly checkups are essential for diagnosing oral diseases early. When it comes to treatments fillings and crowns are common for tooth decay, but according to me, preventive care like fluoride use is the real game-changer. Dentists often detect problems long before patients feel discomfort, proving why routine care is a cornerstone of oral health.
Conclusion
The 9 common dental diseases from cavities to oral cancer, affect millions of Americans each year. Dental diseases can be overwhelming, but in my opinion, regular checkups and small daily habits are the easiest ways to stay ahead. A healthy mouth leads to a healthier body, and the best time to act is now.
FAQs
Q1: What are the most common dental diseases in adults?
The most common dental diseases include tooth decay, gum disease, tooth sensitivity, and oral cancer, affecting millions of U.S. adults.
Q2: How can I prevent cavities and gum disease naturally?
Prevent cavities and gum disease with daily brushing, flossing, fluoride toothpaste, balanced nutrition, and regular dentist visits.
Q3: What are early warning signs of dental problems?
Watch for toothache, bleeding gums, persistent bad breath (halitosis), or tooth sensitivity, these may indicate early oral infection.
Q4: Can untreated dental problems cause serious health issues?
Yes. Untreated dental diseases can lead to periodontitis, dental abscess, and systemic infections that may affect heart health.
Q5: How often should I visit a dentist to avoid oral health problems?
Most dentists recommend a checkup every 6 months for early detection and treatment of cavities or gum disease.
