What is Glutathione and How Does it Work in the Body?
Glutathione and skin whitening have become increasingly popular in the world of skincare and beauty. This powerful antioxidant is naturally produced in the body and plays a key role in detoxification and cellular protection. But beyond health benefits, glutathione has gained attention for its ability to lighten skin tone, reduce hyperpigmentation, and promote a brighter, more even complexion. Studies suggest that consistent use of oral glutathione can lead to visible improvements in skin clarity by blocking melanin production. With rising demand for natural alternatives to harsh whitening agents, glutathione stands out as a safe skin lightening solution backed by research and real-world results. Why is glutathione so important?

Without enough glutathione, the body struggles to neutralize toxins. Low levels are linked to diseases, poor immunity, and early aging. Increasing glutathione can promote clear skin, boost energy, and improve overall wellness. That’s why it’s gaining popularity in both health and beauty circles.
Glutathione As a Skin Whitening Agent: What Science Says?
Glutathione can lighten the skin by stopping melanin production. It blocks an enzyme called tyrosinase, which helps create melanin, the dark pigment in skin. This process is called tyrosinase inhibition. At the same time, it encourages a switch from eumelanin (dark pigment) to pheomelanin (light pigment). Over time, this results in a more even and lighter skin tone.
Clinical trials show that oral glutathione at 250mg/day can decrease the melanin index. These studies found improvements in skin tone, smoothness, and glow after 8–12 weeks. Results vary depending on skin type, dosage, and lifestyle habits. IV and topical options are also used but carry risks not present in oral forms.
How Long Does It Take to See Skin Whitening Results?
The timeline to see visible skin whitening results from glutathione can vary depending on several factors, including your melanin index, method of administration (oral, IV, or topical), dosage, consistency, and individual metabolism. On average, most users report noticeable improvements in skin brightness and reduced hyperpigmentation within 4 to 12 weeks of regular use.
According to a 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted in the U.S., participants taking 250 mg/day GSH showed significant pigment modulation and improved biophysical skin parameters such as skin elasticity and ultraviolet spot reduction by week 8.
Factors That Affect Results Timeline
- Dosage & Consistency
Lower doses (like 250–500 mg/day) may take longer to show results, while higher doses may accelerate effects. However, studies have proven efficacy at lower than 500 mg dose levels too. - Skin Type & Melanin Levels
Individuals with higher eumelanin content may take longer to see visible changes due to stronger pigmentation. Glutathione works by shifting eumelanin to pheomelanin, a lighter pigment, but this process is gradual. - Method of Intake
Oral glutathione is well tolerated, but it may take more time than IV due to slower absorption. IV administration can result in faster onset but comes with safety concerns. - Lifestyle & Diet
A glutathione-rich diet (including spinach, avocados, and turmeric) and reduced sun exposure can significantly boost the results.
Anti-Aging and Antimelanogenic Properties of Glutathione
Glutathione, often referred to as the “master antioxidant,” plays a crucial role in both anti-aging and skin-lightening (antimelanogenic) processes. It exists in its active form as reduced glutathione (GSH) and is naturally produced in the body. However, as we age, the body’s glutathione levels decline, leading to increased oxidative stress, which contributes to the development of fine lines, wrinkles, and other signs of aging.
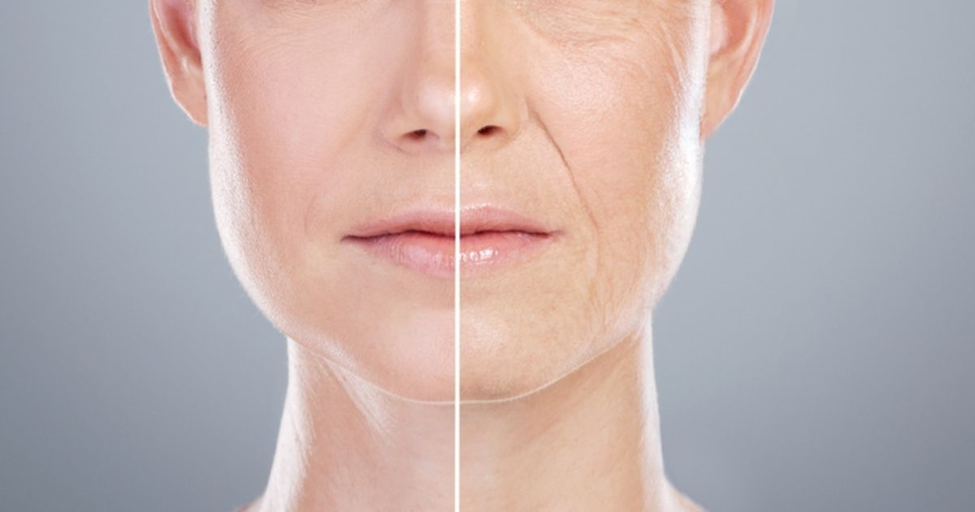
Anti-Aging Benefits
Glutathione combats free radicals unstable molecules that damage skin cells and accelerate aging. By neutralizing these free radicals, glutathione helps:
- Reduce the appearance of wrinkles
- Improve skin elasticity
- Promote a smoother, more youthful skin texture
Clinical studies have shown that individuals taking oral GSH supplements over several weeks to months experience visible improvements in wrinkle depth and overall skin condition.
Antimelanogenic (Skin Lightening) Effects
Glutathione also exhibits significant antimelanogenic properties by:
- Inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production, which helps reduce existing hyperpigmentation and prevent the formation of new dark spots.
- Altering melanin synthesis, shifting the production from eumelanin (a darker pigment) to pheomelanin (a lighter pigment), leading to a brighter and more even skin tone.
A 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial involving 250 mg/day of oral GSH supplementation demonstrated notable improvements in skin properties, including a reduction in ultraviolet-induced spots, which are common markers of photoaging.
Is Glutathione Better Than Collagen for Anti-Aging?
When it comes to anti-aging, both glutathione and collagen offer impressive benefits, but they work differently in the body. Glutathione, known for its potent antioxidant power, protects skin cells from oxidative damage. It reduces the appearance of wrinkles, improves skin elasticity, and enhances overall radiance by fighting free radicals and minimizing ultraviolet spots. Additionally, glutathione offers depigmentation benefits by reducing melanin formation through tyrosinase inhibition and shifting eumelanin → pheomelanin, making skin appear brighter and more youthful.
Collagen, on the other hand, is a structural protein that keeps your skin firm, smooth, and plump. As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to sagging and wrinkles. Supplementing with collagen can help restore skin elasticity and moisture levels, but it doesn’t directly affect pigment modulation or melanin index like glutathione does.
In terms of clinical evidence, studies on glutathione show wrinkle reduction significance, skin property improvements from oral administration, and safety in doses as low as 250 mg/day GSH. While collagen is effective for firmness, glutathione offers both anti-aging and skin lightening, a dual benefit collagen alone cannot match.
Glutathione in Clinical Trials and Research
One of the most cited studies is a 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial where participants took 250 mg/day of oral glutathione. The study showed statistically significant improvements in skin lightness, elasticity, and reduction in fine lines. Both GSH and GSSG forms were tested and proven safe.
Results were measured using devices that checked melanin index, elasticity, and hydration. No serious side effects were reported. Researchers concluded that glutathione is both effective and safe at lower doses.
What Makes These Studies Reliable?
The trials used high standards, placebos, blind testing, and strict controls. The outcomes weren’t just self-reported; they were scientifically measured. This level of testing gives weight to claims about glutathione’s benefits.
Is Glutathione Safe for Daily Use?
Yes, oral glutathione is generally safe when taken as directed. Clinical studies support 250 mg/day as both effective and low-risk. High doses or IV use should be monitored by healthcare providers. The oral form allows gradual changes and is easier to tolerate.
It’s also important to maintain a healthy liver and kidneys, as they help process glutathione. Side effects are rare but may include mild stomach upset or allergic reactions. Always choose reputable brands and avoid unregulated injections.
Who Should Avoid Glutathione?
Pregnant or breastfeeding women, people on chemotherapy, or those with liver/kidney disorders should consult a doctor first. If you’re taking other medications, it’s best to ask about interactions. Never self-inject glutathione without supervision.
Routes of Administration: Oral vs IV vs Topical
Oral glutathione is the safest and most studied form. It’s easy to take, widely available, and effective over time. IV glutathione delivers faster results but carries risks like infection and allergic reactions. Topical creams may lighten the skin locally but don’t offer full-body effects.
Each Route has its Pros and Cons
| Route | Pros | Cons |
| Oral | Safe, easy, long-term results | Slower visible effects |
| IV | Fast results | Risky, needs supervision |
| Topical | Easy to apply | Local effect only |
Which One is Best for You?
Choose oral if you want a safe, gradual effect. IV may be suitable for medical use under supervision. Topical options work for small areas but won’t change overall skin tone. Pairing oral glutathione with vitamin C boosts its effects.
Myths and Misconceptions About Glutathione
Many people believe glutathione works overnight or that it bleaches the skin. These are myths. It doesn’t bleach, it reduces melanin production gradually and naturally. Others fear it’s dangerous. In reality, oral forms are safe when used properly.
Some claim it works for everyone the same way. That’s false genetics, lifestyle, and metabolism all play a role. Another myth is that once you stop, your skin darkens again. Truth is, if you maintain a healthy routine and sun care, results can last.
Should You Worry About Side Effects?
No major side effects are reported in studies when taken at 250–500 mg/day. Stick to recommended dosages and avoid unverified brands. Consult a doctor if you’re unsure about your health status.
Combination with Other Skincare Agents
Glutathione works best when paired with vitamin C, which helps it stay active longer in the body. Together, they amplify antioxidant effects and enhance skin glow. Some users combine it with collagen, hyaluronic acid, or niacinamide for better hydration and texture.
Avoid combining with products that irritate the skin like strong acids or bleaching agents. These can trigger sensitivity and reduce the benefits.
Best Combo Routines
- Morning: Glutathione + Vitamin C + Sunscreen
- Night: Niacinamide + Moisturizer + Collagen
- Stay hydrated and eat antioxidant-rich foods to support your routine.

Dosage Recommendations and How to Use It Safely
For daily use, 250–500 mg/day of oral glutathione is recommended. Take it on an empty stomach with vitamin C for best absorption. Some users divide doses throughout the day, like morning and evening.
Don’t exceed the dose without medical advice. Also, take breaks every few months to assess your skin’s condition. Always choose FDA-approved brands and avoid suspicious IV injections or whitening drips sold online.
Tips for Better Results
- Drink 8–10 glasses of water daily
- Use sunscreen every day
- Eat antioxidant-rich foods like berries and leafy greens
- Exercise regularly and sleep well
Who Can Benefit Most from Glutathione?
Anyone dealing with hyperpigmentation, uneven skin tone, age spots, or dull skin can benefit from glutathione. It’s also ideal for people exposed to pollution, stress, or sun damage. Men and women of all ages can safely use it.
Those with skin conditions like melasma, freckles, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation may see gradual improvements. It’s also popular in bridal skincare regimens and pre-event prep.
Should Teens Use Glutathione?
Teens under 18 should avoid supplements unless prescribed. For minor pigmentation, topical treatments and a good skincare routine are better options. Always consult a dermatologist.
Conclusion
Glutathione offers real benefits backed by science. From tyrosinase inhibition to anti-aging, its effects are more than cosmetic. When used properly, it can reduce melanin, brighten your skin, and promote overall wellness. It’s not a miracle product, but it works well over time. Choose oral forms, support it with healthy habits, and avoid unsafe injections. For most people, glutathione is a safe, effective way to enhance skin tone and health naturally. Be patient, stay consistent, and protect your skin from the sun. Glutathione won’t transform you overnight but with time, it will help you glow from within.
FAQs
Q: How long does glutathione take for skin whitening?
A: Visible skin whitening results may appear in 4 to 12 weeks with regular use of glutathione, depending on the dosage and individual response.
Q: What is the mechanism of action of glutathione in skin whitening?
A: Glutathione works by inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme responsible for melanin production, and shifts eumelanin to pheomelanin, leading to lighter skin.
Q: How much glutathione do I need for skin whitening?
A: Most studies show that a daily dose of 250–500 mg of reduced glutathione (GSH) is effective for skin whitening without serious side effects.
Q: Which glutathione is best for skin whitening?
A: Reduced glutathione (GSH) in liposomal or sublingual form is considered most effective due to better absorption and bioavailability.

 Medically reviewed by
Medically reviewed by