Did you known that in America alone, more than 34 million people are living with diabetes and because of this most of them need insulin treatment as a way of controlling this disease? Medical professionals have made significant progress in the fight against diabetes which provides many terms on offering an individual a way to take control of their condition and even live a healthier life. Insulin treatment is a significant part of treatment of diabetes to many people and can help control blood sugar in the body.
Understanding Insulin Therapy Basic
Insulin therapy is a vital treatment of diabetes which involves usage of insulin in order to control the level of sugar in the blood. People with diabetes will absolutely require this treatment because it will help in the absorption of glucose in cells and thus reducing blood sugar.
What is Insulin and How does it Works?
Insulin is a hormone that is secreted by the pancreas and it is crucial in the regulation of glucose. Once you take food, your body changes food into glucose and the glucose enters the blood stream. Insulin enables the cells to take up the glucose, and this is a source of energy and a healthy level of blood sugar. In diabetes, insulin is not produced in adequate quantities or cannot be used by the body, so it requires insulin therapy.
The Role of Insulin in Blood Sugar Regulation
The injections containing insulin assist in controlling the level of blood sugar as it acts in the same case as natural insulin the human body produces. Through insulin, diabetic patients can promote the cellular intake of glucose, which lowers their sugar content in the blood. Insulin treatment requires a balance between the amounts of insulin and dietary and physical activity to achieve the best glucose balance in the blood.
| Insulin Type | Action Time | Role in Blood Sugar Regulation |
| Rapid-Acting Insulin | 15 minutes to 4 hours | Controls post-meal blood sugar spikes |
| Long-Acting Insulin | Several hours to a day or more | Provides background insulin levels between meals and overnight |
With the right insulin treatment, it is expected to have the same quality of life as healthy people provided with diabetes individuals have the ability to control the treatment resulting in the aspect of mood improvement, avoiding having complications in the future. Principles of basic insulin therapy are essential to getting control of diabetes. Understanding the process of insulin and its activity in the normalization of blood sugar levels allows people to better orient in the treatment course.
Why is Insulin Therapy Necessary?
Insulin therapy is necessitated by the fact that the body cannot produce insulin or utilize it efficiently, a hormone that plays the important role of regulating glucose levels. Insulin treatment then becomes an indispensable remedy to the treatment of diabetes when other methods do not seem to work in controlling the level of blood sugar.
Lifelong Insulin Requirements in Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune problem in which the immune system of a body destroys the insulin-secreting beta cells of the pancreas. Consequentially, individuals who suffer Type 1 diabetes cannot produce insulin and to maintain the level of glucose in their blood they need to take insulin throughout their life. The calculation of the doses of insulin plays a significant part in this regard because it directly affects the success of the medication as well as the control of the illness.
Progressive Requirement of Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes
Diabetes types 2 are accompanied by insulin resistance and the inability of insulin. The capabilities of the pancreas to secrete insulin may decrease in the course of time, so a lot of persons may require insulin during that process. Type 2 diabetes is progressive so insulin treatment may be implemented at any of its stages due to the reaction of an individual to the obtained treatment and evolution of his or her illness.
Acute Insulin Need in Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes arises during pregnancy and it normally occurs in the second or third trimester because of insulin resistance and hormonal changes. Gestational diabetes can be treated with proper dieting and exercise, although some pregnant women may also need to take insulin to ensure the regulation of the level of sugar in the blood. This requirement is mostly a short-term process and dissipates following pregnancy; it is however instrumental to the wellbeing of the health of the mother and the infant.
Special Situations Requiring Insulin Therapy
Other than the usual types of diabetes there are special cases where the use of insulin therapy becomes unavoidable. An example is people who have been operating, have been severally infected or are taking drugs that alter their blood sugars whereby temporary insulin therapy becomes a necessity. It is necessary to be informed about insulin varieties that include rapid- acting insulin, short- acting insulin, intermediate- acting insulin and long acting insulin in order to adjust the insulin therapy to the needs of the person.
Insulin is of vital importance in diabetes treatment and is applicable towards most types of the condition and other situations. The correct calculation of the insulin doses and the right choice of insulin varieties are the keystones on the way to good glycemic control and the prevention of diabetes-related complications.
Types of Insulin and Treatment Regimens
Knowledge of various forms of insulin and types of treatment is essential in being an effective manager of diabetes.
Short-Acting, Rapid-Acting, Intermediate-Acting and Long-Acting Insulin
There are different types of insulin classified according to the stage of onset and action. Rapid acted insulin starts to act within 15 minutes of administration and it is thus preferred in meal time glucose control. Short-acting insulin is recommended to have slightly delayed insulin action, they are generally used alongside longer-acting insulin. The rate of onset of intermediate-acting insulin is slower and the insulin is commonly used to provide basal insulin coverage. Long-acting insulin has a prolonged duration of action it keeps the insulin level in the body constant over a long duration of time, typically 24-hours or even more, which is a basal insulin supplying process.
Ready-mix Insulin Products
Premixed insulin preparations are mixtures of different insulin, e.g. short-acting and intermediate-acting insulin in the same vial or pen. The formulations make the injection process easy since they require a smaller number of injections. Premixed insulin’s make life easier, especially when an individual has a difficult time with complex regimens or when an individual cannot mix insulin personally.
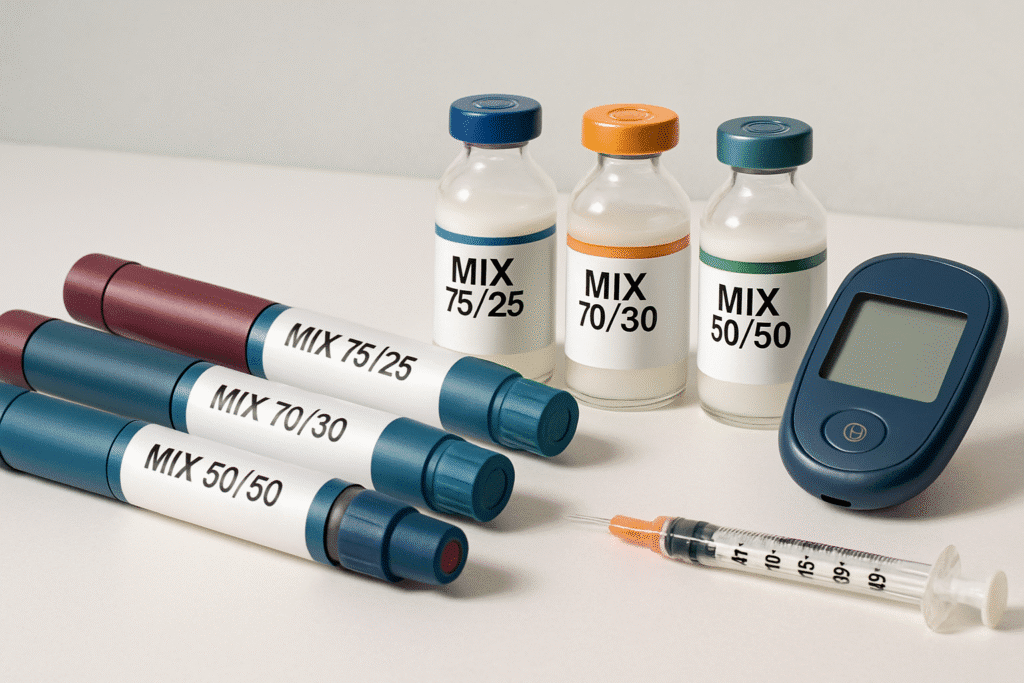
Other Common Insulin Regimens Such as Basal-Bolus
Basal-bolus insulin regimen is a method of treatment which is flexible and resembles the natural insulin production of the body. It entails the use of long- acting insulin (basal) that is used to maintain basal levels of insulin and fast-acting insulin (bolus) before meals to control post meal surges of glucose. Other regimens are incorporation of premixed insulin twice in a day or highly developed regimens such as injection of several injections of varying types of insulin. The perfected mechanism of fast insulin delivery is insulin pump therapy, which gives continuous infusion of rapid-acting insulin during daytime hours, with doses added at meal time.
Duration of Different Insulin Types
Different types can last numerous hours with an average of 3 to 10 hours. The advantage is that rapid-acting insulin has duration of about 3-5 hours, and short-running ones have duration of 6-8 hours. Intermediate-acting insulin stay active between 12 and 18 hours while long acting insulin take 24 hours or more. It is vital to understand these durations to plan the insulin regimens and to prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Administering Your Insulin Therapy
In order to cope with diabetes, it is necessary to know how to perform insulin treatment. Proper insulin administration also requires one to have knowledge of how to handle insulin equipment and procedures in order to achieve the best blood sugar levels.
Insulin Injection Practices and Ideal Techniques
Effective management of diabetes requires proper injection technique of insulin. This includes implementation of appropriate length of the needle, at what angle it should be inserted, and whether it injects insulin into the subcutaneous tissue. Insulin injection into the belly, thighs and buttocks is advised because these body parts have more fat and thus injecting the insulin beneath the skin will be easier. Changing the sites of injections in those areas in rotation may be useful way to avert the signs of the so called lipodystrophy where the fat underneath the skin is not evenly distributed.
Device Features in Delivery of Insulin Pens, Syringes, and Pumps
There are a number of insulin delivery devices, each of which has its pros. Insulin pens are user-friendly and can be carried around very easily. They have the benefits of flexibility in dose size, and are typically lower in cost than pens. Insulin pumps allow a continuous delivery of insulin that can be set to vary throughout the day, and can thus deliver better control of blood glucose levels.
| Device | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Insulin Pens | Convenient, portable, easy to use | May be more expensive than syringes |
| Syringes | Flexible dosing, cost-effective | Requires manual drawing of insulin |
| Insulin Pumps | Continuous insulin delivery, programmable basal rates | Requires training, can be bulky |
Injection Site Rotation and Injection Management
Due to the risk of developing Lipodystrophy and to maintain steady levels of insulin absorption, it is crucial to rotate the injection sites. This can be handled with a methodical plan of site rotation. To give an example, rotation in areas of injection could be helpful to divide it into sections. One should also maintain an inventory of injection points so that there is rotation.
Storage and Travel with Insulin
Insulin should also be stored well to ensure it is potent. Vials of insulin or pens that have not been opened must be kept in the fridge. After being opened, they may be allowed to stay up to a given time and this time is normally up to 30 days depending on the instructions of the manufacturer. Traveling with insulin, taking care of it to be cooled down, insulated bags, ice packs, may be needed, and carrying extra supplies in case of unplanned delays is necessary.
Living Successfully with Insulin Therapy
Data has shown that to ensure good glycemic control, it is important to learn how to manage insulin therapy among diabetic patients hence enhancing their quality of life. This includes learning ways to measure and alter the insulin dose, control the condition of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and plan the insulin usage in conjunction with the intake of food and exercise.
Calculating and Adjusting Insulin Doses
The amount of insulin to be injected is also calculated based on different factors such as the blood glucose levels in the body, diet plans and level of physical exercises. To ensure that it is a safe, you have to work with a medical expert to create an individualized dosing plan. Constant observation of the blood sugar level aids in regulation of dosages in a bid to get an optimum glycemic control.
Managing Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
Since a person receiving insulin treatment must cope with both low and high blood sugar, it is important to manage the condition. It is important to know the symptoms of these conditions and what to do in the case of an emergency. In hypoglycemia, fast-acting carbohydrates will be useful and in hyperglycemia, a change in insulin dosage or other medication.
Coordinating Insulin with Diet and Exercise
It is useful to coordinate management strategies through insulin therapy, exercise, and diet. This can be by way of a balanced diet that considers the quantities of carbohydrates being consumed and also by being physically active. It is also necessary to determine a correction of the insulin depending on the changes in the food intake and physical activity.
- Plan snacks and meal ahead of time, carb content take into account.
- Take part in physical exercise regularly, and modify insulin levels when necessary.
- Observe the levels of blood glucose prior to, during, and soon after exercise.
Conclusion
Insulin therapy is an essential aspect of treatment among diabetics as it helps them in getting control over their blood sugar. With this knowledge of insulin treatment, its types, and regimens, people may get under control of their diabetes status.
The close cooperation with the healthcare providers is required to optimize the use of insulin therapy. Among these are figuring out and modifying the insulin doses, hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and combining insulin with diet and activity. With such action, people are able to control their level of sugar in blood and control possible complications of diabetes.
When one gets the right advice and encouragement, it is possible to live with diabetes and even control this condition with a combined insulin therapy. Remaining educated and involved in their treatment, people will be able to enhance their well-being and quality of life and live well with diabetes.
FAQ’s
Q1. What is the main aim of using insulin in the treatment of diabetes?
The main idea of insulin therapy is to assist in balancing blood sugar by mediating the uptake of glucose in the cells thereby reducing the blood sugar amount in the body and balancing diabetes.
Q2. How can I find the right amount of insulin to use?
Setting appropriate dose of insulin entails the efforts of calculating the specific insulin needs according to the factors like food intake, exercise and the current glycemic levels with the help of medical practitioner.
Q3. What are the varieties of insulin used in the management of diabetes?
There are some forms of insulin such as rapid-acting insulin, short-acting insulin, intermediate-acting insulin, long-acting insulin, and premixed insulin with specific onset and durations of effects.
Q4. What is the proper way to do insulin injections?
When giving yourself insulin injections, the correct process should be done by adhering to the methods of injection, rotating injected spots, and applying proper gadgets like insulin pens, syringes, or insulin pumps as suggested by your doctor.
Q5. What are the positive aspects of using insulin pump in the management of diabetes?
Advantages of insulin pump Therapy are increased control of the dosage of insulin, greater freedom to control the blood sugar levels, and the likely reduction in the volumes of blood sugar levels, can also be seen as an advantage.

 Medically reviewed by
Medically reviewed by