Have you ever applied your favorite skincare products, only to feel an unexpected burning or stinging sensation? If your face feels like it’s on fire after your routine, you’re not alone. Many people experience this discomfort, but the reasons can vary from sensitive skin and harsh ingredients to compromised skin barriers or allergic reactions.
Sensitive or Irritated Skin
What it Means
Sensitive skin is a condition in which the skin has a lower tolerance to external factors such as skincare products, environmental conditions (like wind, sun, or pollution), and even stress or hormonal changes. People with sensitive skin often experience sensations like burning, stinging, itching, or tightness sometimes without any visible signs of irritation such as redness or rash. In some cases, however, symptoms may include visible inflammation, dryness, or flaking.
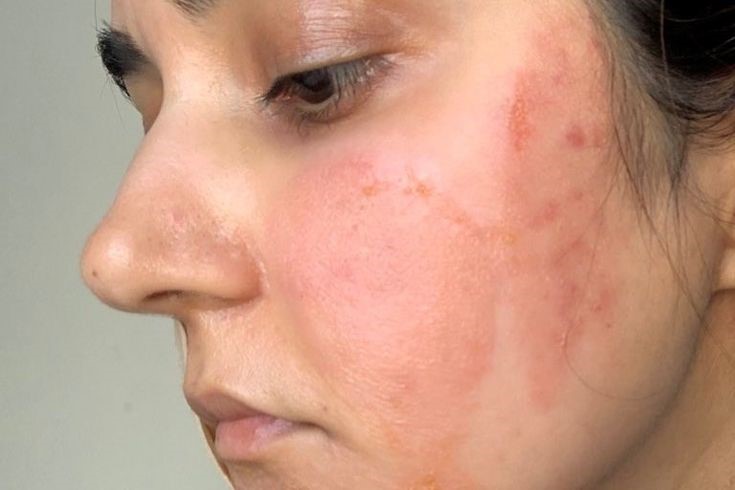
Evidence
- TRPV1 receptors, found on sensory nerves in the skin, are more active in sensitive skin. These receptors react to heat, acids, and chemicals and are responsible for the burning sensation.
- Research published in Cosmetics journal confirms that sensitive skin shows an increased expression of TRPV1 and a weaker skin barrier, leading to hyperactivity.
Harsh or Strong Ingredients
What it Means
Certain active skincare ingredients such as retinoids, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), benzoyl peroxide, and high concentrations of vitamin C are known for their powerful effects on the skin. These ingredients promote exfoliation, increase cell turnover, or target acne and pigmentation.
If your skin is not accustomed to them, or if they’re introduced too quickly or in high concentrations, they can cause temporary irritation. Common symptoms include burning, stinging, tingling, redness, or dryness. This reaction doesn’t always indicate an allergy rather, it may be your skin’s way of adjusting to the active compounds.
Evidence
- Retinoids and AHAs are known to activate TRPV1 pain receptors, resulting in burning and stinging in some individuals.
- A study published in Skin Pharmacology and Physiology found that even common preservatives like phenoxyethanol can trigger burning by activating TRPV1.
Allergic Reaction
What it Means
An allergic reaction occurs when your immune system identifies a substance often an ingredient in a skincare or cosmetic product as harmful, even if it isn’t for most people. This immune response can trigger symptoms such as burning, itching, redness, swelling, hives, or a visible rash.
Importantly, allergic reactions can happen even with products labeled “hypoallergenic,” as these labels are not regulated and don’t guarantee the product is free of all potential allergens.
Evidence
- The American Academy of Dermatology recognizes allergic contact dermatitis as a common cause of burning skin after applying cosmetics, especially those with fragrances, preservatives, and botanical extracts.
- Patch testing helps identify ingredients causing these reactions, according to studies in dermatological practice.
Damaged Skin Barrier
What it Means
The skin barrier, also known as the stratum corneum, is the outermost layer of the skin. It serves as a critical protective shield keeping moisture in and blocking out irritants, bacteria, and environmental aggressors.
When this barrier is compromised often due to over cleansing, excessive exfoliation, harsh skincare ingredients, or environmental stressors the skin loses its ability to retain moisture and defend itself. As a result, it may become dry, tight, red, inflamed, sensitive, or experience a burning or stinging sensation.
A damaged barrier needs time and proper care to heal. Using gentle, hydrating, and barrier repairing ingredients like ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and fatty acids can help restore its function.
Evidence
- A compromised skin barrier leads to increased transepidermal water loss (TEWL), allowing irritants to penetrate more deeply and activate nerves.
- Animal studies shows that activation of TRPV1 delays skin barrier repair, while blocking TRPV1 speeds up healing.
Mixing Incompatible Products
What it Means
Combining multiple active ingredients in the same skincare routine such as retinol with vitamin C, or layering alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) with beta hydroxy acids (BHAs) can overwhelm the skin. These potent actives may have different pH levels or mechanisms of action that, when used together, increase the risk of irritation, dryness, redness, or a burning sensation.
While each ingredient may be effective on its own, using them simultaneously especially without proper spacing or layering can disrupt the skin’s balance and compromise its barrier. To avoid adverse reactions, it’s important to understand which ingredients work well together and introduce new actives gradually.
Evidence
- Combining too many actives increases oxidative stress and disrupts the skin’s natural pH, weakening the skin’s barrier.
- Skincare experts recommend introducing one active ingredient at a time, especially when starting a new routine, to avoid skin sensitization.
Teen vs Adult Burning After Skincare
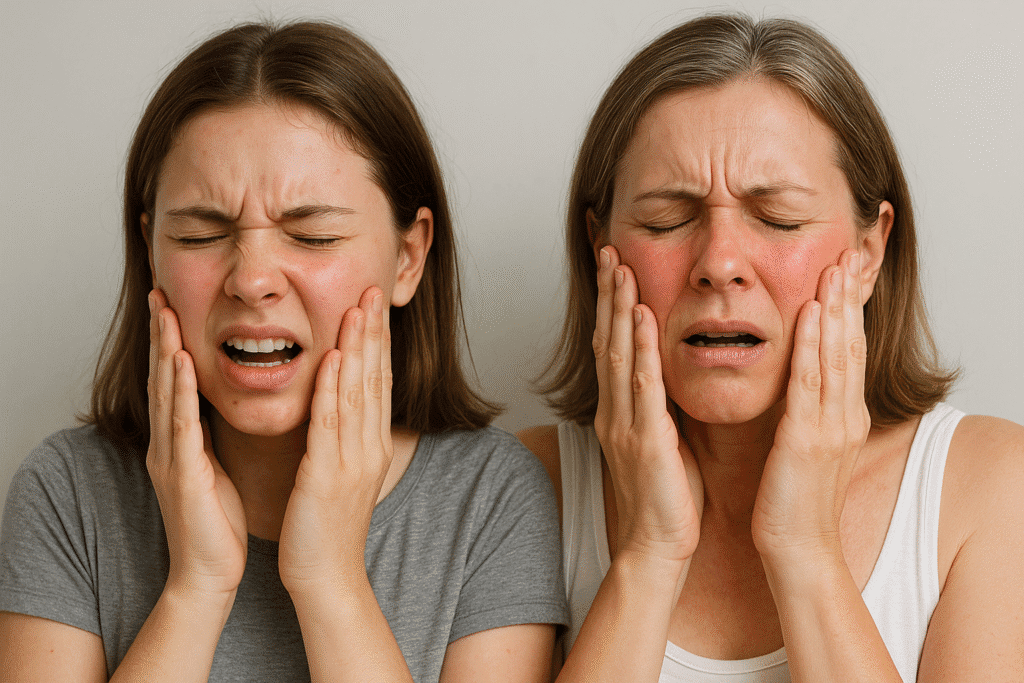

|
Aspect |
Adults |
|
| Skin Type | Usually oilier, more resilient, higher sebum production | Often drier, thinner skin, especially after age 30 |
| Common Triggers | Acne treatments: benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, alcohol-based products | Anti-aging products: retinoids, AHAs, and vitamin C |
| Burning Frequency | Less frequent unless overusing acne products | More common due to aging skin, thinning barrier, and ingredient overload |
| Skin Barrier Strength | Typically stronger; recovers faster | Weaker barrier function, slower recovery from irritation |
| Hormonal Impact | Active sebaceous glands; hormonal acne may lead to overuse of harsh products | Hormonal shifts (e.g., perimenopause) may increase sensitivity |
| Tendency to Overuse Products | High due to acne concerns and misinformation | Moderate often trying multiple actives for anti-aging |
| Typical Mistake | Using too many harsh, drying products at once | Layering multiple active ingredients without spacing |
| Response to Irritation | May resolve quickly once stopped | Longer healing time due to decreased collagen and lipid levels |
| Product Suitability | Non comedogenic, fragrance free, gentle exfoliants recommended | Barrier repairing, hydrating, and anti-inflammatory products preferred |
| Clinical Advice | Avoid alcohol based toners, harsh scrubs | Avoid over exfoliation, start with low strength actives |
Immediate Relief: How to Soothe Burning Skin?
Rinse with Cool Water
If the burning starts right after application, gently rinse your face with lukewarm or cool water to remove any irritating product. Avoid hot water, as it can worsen inflammation.
Apply a Soothing Moisturizer
Look for calming ingredients like:
– Aloe Vera (natural anti-inflammatory)
– Centella asiatica (Cica) (heals and reduces redness)
– Panthenol (Vitamin B5) (repairs the skin barrier)
– Oat extract (relieves itching and irritation)
Use a Cold Compress
Wrap an ice pack in a clean cloth or soak a soft towel in cold water and press it gently onto irritated areas for a few minutes to reduce heat and redness.
Skip Active Ingredients Temporarily
Avoid exfoliants (AHAs/BHAs), retinoids, and vitamin C until your skin fully recovers. Stick to a gentle cleanser and moisturizer.
Try a Healing Occlusive
If your skin is very sensitive, apply a thin layer of petroleum jelly (Vaseline) or a fragrance-free balm to lock in moisture and protect your skin barrier.
How to Prevent Burning Skin in the Future?

Patch Test New Products
Before applying a new product all over your face, test it on a small area (like behind your ear or inner forearm) and wait 24 hours to check for reactions.
Check for Harsh Ingredients
Common irritants include:
- Alcohol (denatured alcohol, SD alcohol)
- Fragrances & essential oils
- Strong acids (high % glycolic/lactic acid)
- Retinoids (if used incorrectly)
If your skin is sensitive, opt for fragrance-free, alcohol-free, and hypoallergenic formulas.
Don’t Over Exfoliate
Using too many exfoliating acids or physical scrubs can strip your skin’s protective barrier. Stick to 1-2 times per week if you have sensitive skin.
Apply Products on Damp Skin (For Some Actives)
Some ingredients (like hyaluronic acid) work better on damp skin, but others (like retinoids and strong acids) should be applied to dry skin to minimize irritation.
Strengthen Your Skin Barrier
Use ceramides, fatty acids, and cholesterol-rich moisturizers to repair and protect your skin from sensitivity.
Consult a Dermatologist if Burning Persists
If your skin keeps reacting badly, you might have an underlying condition like rosacea, eczema, or contact dermatitis. A dermatologist can help identify triggers and recommend safe products.
Conclusion
Burning after skincare is usually a sign that your skin is irritated or damaged. By identifying the cause and adjusting your routine, you can keep your skin calm, healthy, and glowing. Always listen to your skin if something stings, it’s trying to tell you something.

 Medically reviewed by
Medically reviewed by