Introduction
In recent years, the concept of an alkaline vegan diet has gained substantial attention in health and wellness circles. Rooted in the belief that certain foods can impact the body’s pH levels, proponents of this dietary approach advocate for consuming predominantly alkaline-forming foods to achieve better health and vitality. Let’s delve into the fundamentals, benefits, and considerations surrounding the alkaline vegan diet.

Table of Contents
Understanding the Basics
The alkaline diet revolves around the pH scale, which measures the acidity or alkalinity of substances on a scale of 0 to 14. A pH level below 7 is considered acidic, while a level above 7 is alkaline. Proponents of the alkaline diet argue that by consuming primarily alkaline-forming foods, the body’s pH balance can be optimized, leading to various health benefits.
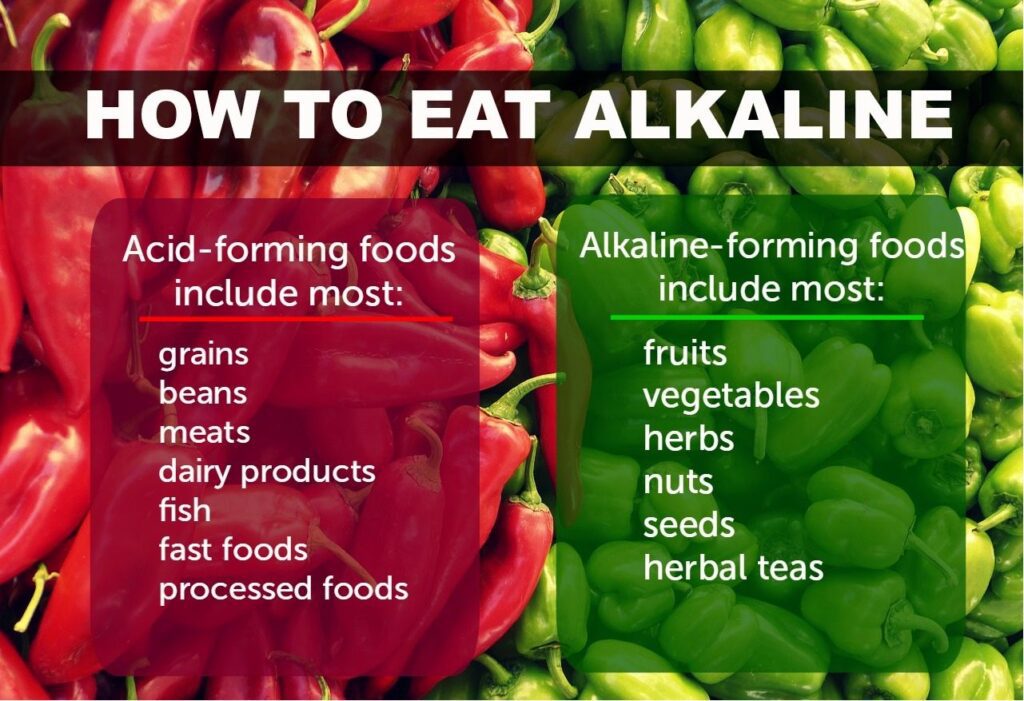
Alkaline Forming Food
1. Leafy Greens
Spinach: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and chlorophyll, spinach is highly alkaline and versatile in various dishes.
Kale: Packed with antioxidants, fiber, and nutrients, kale is a powerhouse alkaline vegetable.
Swiss Chard: Another nutrient-dense leafy green that supports alkalinity in the body.
2. Cruciferous Vegetables
Broccoli: A cruciferous vegetable high in fiber, antioxidants, and vitamins, contributing to an alkaline environment.
Brussels Sprouts: These are not only alkaline but also provide essential nutrients like vitamin C and vitamin K.
3. Citrus Fruits
Lemons: Despite their acidic nature outside the body, lemons are considered highly alkaline-forming due to their mineral content.
Limes: Similar to lemons, limes have alkaline properties once metabolized.
4. Root Vegetables
Beets: These are known for their alkalizing effect on the body and are rich in antioxidants and dietary fiber.
Sweet Potatoes: With a host of vitamins and fiber, sweet potatoes contribute to an alkaline diet.
5. Other Alkaline Foods
Almonds: A source of healthy fats, protein, and minerals, almonds leave an alkaline residue in the body.
Quinoa: A protein-rich grain that is alkaline-forming and gluten-free, making it a popular choice in alkaline diets.
Avocado: Rich in healthy fats and nutrients, avocados are alkaline and versatile in various dishes.
6. Healthy Oils
Olive Oil: This heart-healthy oil has alkaline properties and is often used in cooking and salad dressings.
Coconut Oil: While debated for its alkaline effects, some sources suggest it contributes to alkalinity.
7. Legumes
Chickpeas: High in protein and fiber, chickpeas support an alkaline environment in the body.
Lentils: A good source of plant-based protein and minerals, lending alkaline benefits to the diet.
8. Green Tea
Green tea: Although it is a beverage, it’s known for its alkaline properties and abundance of antioxidants.
Including these alkaline-forming foods in your diet can potentially promote a more alkaline environment in the body. However, it’s important to maintain a balanced approach, incorporating these foods alongside other healthy dietary elements while considering individual nutritional needs. Always consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist before making significant changes to your diet.
Benefits of an Alkaline Vegan Diet
The alkaline vegan diet, centered around consuming predominantly alkaline-forming foods from plant-based sources, is purported to offer several potential benefits. While scientific consensus on its profound effects remains debated, proponents suggest various advantages associated with this dietary approach:
1. Improved Digestive Health
Alkaline-rich foods like leafy greens, vegetables, and fruits are typically high in fiber. These fibers aid digestion by promoting regular bowel movements and supporting a healthy gut microbiome, potentially reducing the risk of digestive issues like constipation.
2. Enhanced Energy Levels
Advocates claim that by reducing acidic foods and focusing on alkaline-forming foods, the body’s pH balance may be optimized. This optimization purportedly leads to increased energy levels and reduced fatigue.
3. Potential Weight Management
An alkaline vegan diet encourages the consumption of whole, nutrient-dense foods while discouraging processed and acidic foods. This emphasis on wholesome plant-based nutrition might naturally support weight management efforts by reducing calorie-dense, processed foods.
4. Alkalinity and Disease Prevention
Some proponents suggest that maintaining an alkaline environment in the body may lower the risk of certain chronic diseases, including osteoporosis and kidney stones. However, scientific evidence supporting these claims is inconclusive and requires further research.
5. Increased Intake of Plant-Based Nutrients
A plant-based diet, especially when focused on alkaline-forming foods, often results in a higher intake of essential nutrients, antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals found abundantly in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds.
6. Potential Anti-inflammatory Effects
Alkaline-rich diets, particularly when centered around whole plant foods, are believed by some to possess anti-inflammatory properties. These properties may potentially alleviate inflammation-related conditions.
7. pH Balance Regulation
While the body has sophisticated mechanisms to maintain its pH balance, proponents suggest that an alkaline diet could assist these natural regulatory processes, helping the body stay within its optimal pH range.
8. Support for Overall Well-being
Adherents often report a general sense of well-being, claiming improvements in skin health, mental clarity, and mood when following an alkaline vegan diet. However, individual responses can vary significantly.
9. Reduced Intake of Processed Foods
By emphasizing whole, plant-based foods, this dietary approach discourages the consumption of processed and refined foods, potentially reducing the intake of unhealthy fats, sugars, and additives.
10. Environmental Impact
Beyond personal health benefits, adopting a plant-based diet, as seen in the alkaline vegan approach, has potential positive environmental implications by reducing the carbon footprint associated with animal agriculture.
Considerations and Criticisms of Alkaline Vegan Diet
While the alkaline vegan diet has gained popularity for its perceived health benefits, it’s also subject to various considerations and criticisms that warrant attention:
1. Lack of Scientific Consensus
Limited Scientific Evidence: The overall scientific consensus on the alkaline diet’s profound effects on health is lacking. Research supporting its claims is limited and often inconclusive regarding its direct impact on the body’s pH levels and health outcomes.
2. Nutrient Balance and Deficiencies
Potential Nutrient Deficiencies: Strict adherence to an alkaline vegan diet might lead to deficiencies in critical nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, calcium, and others typically found in animal-based products. Careful planning and supplementation are often necessary to avoid deficiencies.
3. Individual Variations
Biochemical Individuality: Each person’s body responds differently to dietary changes. What might work well for one individual might not yield the same results for another. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and underlying health conditions can significantly influence outcomes.
4. Acidic Foods’ Importance
Healthy Acidic Foods: Some acidic-forming foods that are restricted in an alkaline diet, like certain whole grains and fruits, offer valuable nutrients. Eliminating these foods completely might lead to a limited nutritional profile and dietary variety.
5. Sustainable Long-Term Adherence
Sustainability of Diet: Adhering strictly to an alkaline vegan diet might be challenging for some individuals over the long term due to social, cultural, or practical reasons. Sustainability is crucial for any dietary change to be effective.
6. Body’s Natural pH Regulation
Body’s pH Regulation: The body has robust mechanisms to regulate its pH levels within a narrow and optimal range. It’s argued that dietary changes have minimal impact on these tightly regulated systems.
7. Alkaline Water and Supplements
Alkaline Water and Supplements: Products like alkaline water or supplements marketed for maintaining an alkaline state might not deliver the promised health benefits. Scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness is limited.
8. Overemphasis on pH
Overemphasis on pH: While pH is crucial in certain bodily functions, focusing solely on the pH of foods might overshadow other essential aspects of a healthy diet, such as adequate hydration, balanced macronutrients, and portion control.
9. Potential Discomfort
Initial Discomfort: Some individuals might experience initial discomfort when transitioning to an alkaline diet, such as digestive changes, as their body adjusts to a different dietary pattern.
10. Impact on Bone Health
Concerns about Bone Health: There are concerns that excessively alkaline diets might negatively impact bone health by affecting calcium metabolism. However, more research is needed to substantiate these claims.
Incorporating an Alkaline Vegan Diet
Incorporating an alkaline vegan diet into your lifestyle can be a gradual and rewarding process. Here are some practical steps to start integrating this dietary approach:

1. Embrace Variety in Plant-Based Foods
Leafy Greens: Make leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard a staple in your meals. Add them to salads, smoothies, or stir-fries.
Colorful Vegetables: Incorporate a variety of vegetables, such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and beets, to diversify your nutrient intake.
Fruits: Include alkaline-forming fruits like lemons, limes, and citrus fruits in your diet. Enjoy them as snacks or use them in cooking.
2. Opt for Whole Grains and Legumes
Quinoa, Millet: Include alkaline whole grains like quinoa and millet in your meals instead of refined grains.
Chickpeas, Lentils: Incorporate legumes like chickpeas and lentils for plant-based protein and alkalinity.
3. Healthy Fats and Oils
Avocado: Use avocado as a healthy fat source in salads, sandwiches, or as a spread.
Olive Oil: Consider using olive oil for cooking or in salad dressings for its alkaline properties.
4. Reduce Acidic Foods
Limit Processed Foods: Cut down on processed and refined foods, which are often acidic. Replace them with whole, unprocessed plant-based options.
Moderate Acidic Foods: While some acidic foods might be restricted in an alkaline diet, moderate consumption of healthy acidic foods like whole grains can be beneficial.
5. Stay Hydrated with Alkaline Beverages
Green Tea: Enjoy alkaline beverages like green tea, which not only hydrate but also contribute to the alkaline environment in the body.
6. Monitor Nutrient Intake
Consult a Professional: Consider consulting a registered dietitian or healthcare professional to ensure you’re meeting your nutritional needs, especially for nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, and calcium.
7. Gradual Transition
Slow Changes: Gradually introduce alkaline foods into your diet rather than making sudden and drastic changes. This gradual approach allows your body to adjust comfortably.
8. Experiment with Alkaline Recipes
Explore Recipes: Search for alkaline vegan recipes online or in cookbooks to find inspiring and delicious meal ideas that align with this dietary approach.
9. Balance Is Key
Variety in Diet: Strive for a well-balanced diet that includes a diverse range of nutrient-dense foods to ensure you’re meeting all your nutritional requirements.
10. Listen to Your Body
Pay Attention: Monitor how your body responds to the dietary changes. Everyone’s body is different, so listen to your body’s cues and adjust accordingly.
11. Lifestyle Considerations
Incorporate Other Healthy Practices: Alongside dietary changes, consider incorporating other healthy lifestyle practices like regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep for overall well-being.
Conclusion
The alkaline vegan diet, centered around alkaline-forming foods and predominantly plant-based nutrition, has piqued interest for its potential health benefits. However, scientific evidence supporting its profound effects on health remains limited. As with any dietary change, it’s essential to approach it mindfully, ensuring a balance of nutrients while considering individual health needs and preferences.
While the alkaline vegan diet may not be a one-size-fits-all solution, exploring and incorporating more whole, plant-based foods can undoubtedly contribute positively to overall health and well-being. As research continues, understanding the nuanced relationship between diet, pH balance, and health will be key to unlocking the full potential of dietary interventions in promoting human health.

2 thoughts on “Exploring the Alkaline Vegan Diet”